The history of the camera can be traced much further back than the introduction of photography. Cameras evolved from thecamera obscura, and continued to change through many generations of photographic technology, including daguerreotypes,calotypes, dry plates, film, and digital cameras.
Camera obscura
Photographic cameras were a development of the camera obscura, a device possibly dating back to the ancient Chinese and ancient Greeks which uses a pinhole or lens to project an image of the scene outside upside-down onto a viewing surface.
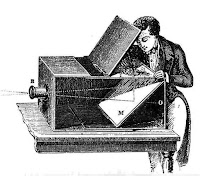 An Arab physicist, Ibn al-Haytham, published his Book of Optics in 1021 AD. He created the first pinhole camera after observing how light traveled through a window shutter. Ibn al-Haytham realized that smaller holes would create sharper images. Ibn al-Haytham is also credited with inventing the first camera obscura.
An Arab physicist, Ibn al-Haytham, published his Book of Optics in 1021 AD. He created the first pinhole camera after observing how light traveled through a window shutter. Ibn al-Haytham realized that smaller holes would create sharper images. Ibn al-Haytham is also credited with inventing the first camera obscura.
On 24 January 1544 mathematician and instrument maker Reiners Gemma Frisius of Leuven University used one to watch a solar eclipse, publishing a diagram of his method in De Radio Astronimica et Geometrico in the following year. In 1558 Giovanni Batista della Porta was the first to recommend the method as an aid to drawing.
Before the invention of photographic processes there was no way to preserve the images produced by these cameras apart from manually tracing them. The earliest cameras were room-sized, with space for one or more people inside; these gradually evolved into more and more compact models such as that by Niépce's time portable handheld cameras suitable for photography were readily available. The first camera that was small and portable enough to be practical for photography was envisioned by Johann Zahn in 1685, though it would be almost 150 years before such an application was possible.
Early fixed images
The first partially successful photograph of a camera image was made in approximately 1816 by Nicéphore Niépce, using a very small camera of his own making and a piece of paper coated with silver chloride, which darkened where it was exposed to light. No means of removing the remaining unaffected silver chloride was known to Niépce, so the photograph was not permanent, eventually becoming entirely darkened by the overall exposure to light necessary for viewing it. In the mid-1820s, Niépce used a sliding wooden box camera made by Parisian opticians Charles and Vincent Chevalier to experiment with photography on surfaces thinly coated with Bitumen of Judea. The bitumen slowly hardened in the brightest areas of the image. The unhardened bitumen was then dissolved away. One of those photographs has survived.

Daguerrotypes and Calotypes
After Niépce's death in 1833, his partner Louis Daguerre continued to experiment and by 1837 had created the first practical photographic process, which he named the daguerreotype and publicly unveiled in 1839. Daguerre treated a silver-plated sheet of copper with iodine vapor to give it a coating of light-sensitive silver iodide. After exposure in the camera, the image was developed by mercury vapor and fixed with a strong solution of ordinary salt (sodium chloride). Henry Fox Talbot perfected a different process, the calotype, in 1840. As commercialized, both processes used very simple cameras consisting of two nested boxes. The rear box had a removable ground glass screen and could slide in and out to adjust the focus. After focusing, the ground glass was replaced with a light-tight holder containing the sensitized plate or paper and the lens was capped. Then the photographer opened the front cover of the holder, uncapped the lens, and counted off as many seconds—or minutes—as the lighting conditions seemed to require before replacing the cap and closing the holder. Despite this mechanical simplicity, high-quality achromatic lenses were standard.
Kodak and the birth of film
 The use of photographic film was pioneered by George Eastman, who started manufacturing paper film in 1885 before switching to celluloid in 1889. His first camera, which he called the "Kodak," was first offered for sale in 1888. It was a very simple box camera with a fixed-focus lens and single shutter speed, which along with its relatively low price appealed to the average consumer. The Kodak came pre-loaded with enough film for 100 exposures and needed to be sent back to the factory for processing and reloading when the roll was finished. By the end of the 19th century Eastman had expanded his lineup to several models including both box and folding cameras.
The use of photographic film was pioneered by George Eastman, who started manufacturing paper film in 1885 before switching to celluloid in 1889. His first camera, which he called the "Kodak," was first offered for sale in 1888. It was a very simple box camera with a fixed-focus lens and single shutter speed, which along with its relatively low price appealed to the average consumer. The Kodak came pre-loaded with enough film for 100 exposures and needed to be sent back to the factory for processing and reloading when the roll was finished. By the end of the 19th century Eastman had expanded his lineup to several models including both box and folding cameras.
In 1900, Eastman took mass-market photography one step further with the Brownie, a simple and very inexpensive box camera that introduced the concept of the snapshot. The Brownie was extremely popular and various models remained on sale until the 1960s.
Film also allowed the movie camera to develop from an expensive toy to a practical commercial tool.
Despite the advances in low-cost photography made possible by Eastman, plate cameras still offered higher-quality prints and remained popular well into the 20th century. To compete with roll film cameras, which offered a larger number of exposures per loading, many inexpensive plate cameras from this era were equipped with magazines to hold several plates at once. Special backs for plate cameras allowing them to use film packs or roll film were also available, as were backs that enabled rollfilm cameras to use plates.
Except for a few special types such as Schmidt cameras, most professional astrographs continued to use plates until the end of the 20th century when electronic photography replaced them.
TLRs and SLRs

The first practical reflex camera was the Franke & Heidecke Rolleiflex medium format TLR of 1928. Though both single- and twin-lens reflex cameras had been available for decades, they were too bulky to achieve much popularity. The Rolleiflex, however, was sufficiently compact to achieve widespread popularity and the medium-format TLR design became popular for both high- and low-end cameras.
A similar revolution in SLR design began in 1933 with the introduction of the Ihagee Exakta, a compact SLR which used 127 rollfilm. This was followed three years later by the first Western SLR to use 135 film, the Kine Exakta (World's first true 35mm SLR was Soviet "Sport" camera, marketed several months before Kine Exakta, though "Sport" used its own film cartridge). The 35mm SLR design gained immediate popularity and there was an explosion of new models and innovative features after World War II. There were also a few 35mm TLRs, the best-known of which was the Contaflex of 1935, but for the most part these met with little success.
The first major post-war SLR innovation was the eye-level viewfinder, which first appeared on the Hungarian Duflex in 1947 and was refined in 1948 with the Contax S, the first camera to use a pentaprism. Prior to this, all SLRs were equipped with waist-level focusing screens. The Duflex was also the first SLR with an instant-return mirror, which prevented the viewfinder from being blacked out after each exposure. This same time period also saw the introduction of the Hasselblad 1600F, which set the standard for medium format SLRs for decades.
In 1952 the Asahi Optical Company (which later became well known for its Pentax cameras) introduced the first Japanese SLR using 135 film, the Asahiflex. Several other Japanese camera makers also entered the SLR market in the 1950s, including Canon, Yashica, and Nikon. Nikon's entry, the Nikon F, had a full line of interchangeable components and accessories and is generally regarded as the first Japanese system camera. It was the F, along with the earlier S series of rangefinder cameras, that helped establish Nikon's reputation as a maker of professional-quality equipment.
Arrival of true digital cameras
By the late 1980s, the technology required to produce truly commercial digital cameras existed. The first true portable digital camera that recorded images as a computerized file was likely the Fuji DS-1P of 1988, which recorded to a 2 MB SRAM memory card that used a battery to keep the data in memory. This camera was never marketed to the public.
The first digital camera of any kind ever sold commercially was possibly the MegaVision Tessera in 1987 though there is not extensive documentation of its sale known. The first portable digital camera that was actually marketed commercially was sold in December 1989 in Japan, the DS-X by Fuji The first commercially available portable digital camera in the United States was the Dycam Model 1, first shipped in November 1990. It was originally a commercial failure because it was black and white, low in resolution, and cost nearly $1,000 (about $2000 in 2014). It later saw modest success when it was re-sold as the Logitech Fotoman in 1992. It used a CCD image sensor, stored pictures digitally, and connected directly to a computer for download.
In 1991, Kodak brought to market the Kodak DCS (Kodak Digital Camera System), the beginning of a long line of professional Kodak DCSSLR cameras that were based in part on film bodies, often Nikons. It used a 1.3 megapixel sensor, had a bulky external digital storage system and was priced at $13,000. At the arrival of the Kodak DCS-200, the Kodak DCS was dubbed Kodak DCS-100.
 The move to digital formats was helped by the formation of the first JPEG and MPEG standards in 1988, which allowed image and video files to be compressed for storage. The first consumer camera with a liquid crystal display on the back was the Casio QV-10 developed by a team led by Hiroyuki Suetaka in 1995. The first camera to use CompactFlash was the Kodak DC-25 in 1996. The first camera that offered the ability to record video clips may have been the Ricoh RDC-1 in 1995.
The move to digital formats was helped by the formation of the first JPEG and MPEG standards in 1988, which allowed image and video files to be compressed for storage. The first consumer camera with a liquid crystal display on the back was the Casio QV-10 developed by a team led by Hiroyuki Suetaka in 1995. The first camera to use CompactFlash was the Kodak DC-25 in 1996. The first camera that offered the ability to record video clips may have been the Ricoh RDC-1 in 1995.
In 1995 Minolta introduced the RD-175, which was based on the Minolta 500si SLR with a splitter and three independent CCDs. This combination delivered 1.75M pixels. The benefit of using an SLR base was the ability to use any existing Minolta AF mount lens. 1999 saw the introduction of the Nikon D1, a 2.74 megapixel camera that was the first digital SLR developed entirely from the ground up by a major manufacturer, and at a cost of under $6,000 at introduction was affordable by professional photographers and high-end consumers. This camera also used Nikon F-mount lenses, which meant film photographers could use many of the same lenses they already owned.
Digital camera sales continued to flourish, driven by technology advances. The digital market segmented into different categories, Compact Digital Still Cameras, Bridge Cameras, Mirrorless Compacts and Digital SLRs. One of the major technology advances was the development of CMOS sensors, which helped drive sensor costs low enough to enable the widespread adoption of camera phones.
Source: Wikipedia
 An Arab physicist, Ibn al-Haytham, published his Book of Optics in 1021 AD. He created the first pinhole camera after observing how light traveled through a window shutter. Ibn al-Haytham realized that smaller holes would create sharper images. Ibn al-Haytham is also credited with inventing the first camera obscura.
An Arab physicist, Ibn al-Haytham, published his Book of Optics in 1021 AD. He created the first pinhole camera after observing how light traveled through a window shutter. Ibn al-Haytham realized that smaller holes would create sharper images. Ibn al-Haytham is also credited with inventing the first camera obscura. The use of photographic film was pioneered by George Eastman, who started manufacturing paper film in 1885 before switching to celluloid in 1889. His first camera, which he called the "Kodak," was first offered for sale in 1888. It was a very simple box camera with a fixed-focus lens and single shutter speed, which along with its relatively low price appealed to the average consumer. The Kodak came pre-loaded with enough film for 100 exposures and needed to be sent back to the factory for processing and reloading when the roll was finished. By the end of the 19th century Eastman had expanded his lineup to several models including both box and folding cameras.
The use of photographic film was pioneered by George Eastman, who started manufacturing paper film in 1885 before switching to celluloid in 1889. His first camera, which he called the "Kodak," was first offered for sale in 1888. It was a very simple box camera with a fixed-focus lens and single shutter speed, which along with its relatively low price appealed to the average consumer. The Kodak came pre-loaded with enough film for 100 exposures and needed to be sent back to the factory for processing and reloading when the roll was finished. By the end of the 19th century Eastman had expanded his lineup to several models including both box and folding cameras. The first practical reflex camera was the Franke & Heidecke Rolleiflex medium format TLR of 1928. Though both single- and twin-lens reflex cameras had been available for decades, they were too bulky to achieve much popularity. The Rolleiflex, however, was sufficiently compact to achieve widespread popularity and the medium-format TLR design became popular for both high- and low-end cameras.
The first practical reflex camera was the Franke & Heidecke Rolleiflex medium format TLR of 1928. Though both single- and twin-lens reflex cameras had been available for decades, they were too bulky to achieve much popularity. The Rolleiflex, however, was sufficiently compact to achieve widespread popularity and the medium-format TLR design became popular for both high- and low-end cameras. The move to digital formats was helped by the formation of the first JPEG and MPEG standards in 1988, which allowed image and video files to be compressed for storage. The first consumer camera with a liquid crystal display on the back was the Casio QV-10 developed by a team led by Hiroyuki Suetaka in 1995. The first camera to use CompactFlash was the Kodak DC-25 in 1996. The first camera that offered the ability to record video clips may have been the Ricoh RDC-1 in 1995.
The move to digital formats was helped by the formation of the first JPEG and MPEG standards in 1988, which allowed image and video files to be compressed for storage. The first consumer camera with a liquid crystal display on the back was the Casio QV-10 developed by a team led by Hiroyuki Suetaka in 1995. The first camera to use CompactFlash was the Kodak DC-25 in 1996. The first camera that offered the ability to record video clips may have been the Ricoh RDC-1 in 1995.






